Beginner’s Guide to Dimensions and Metrics in Google Analytics
by Isaac Wielhouwer | Jul 17, 2024 | Blog, Content
In this brief, informative guide, I will be highlighting the basic essentials of Google Analytics (GA4), providing helpful visuals, and unlocking the key to understanding them in order to get the most out of your marketing insights.
When I first began using Google Analytics, it was difficult to know where to start. The plethora of tabs, tools and ways to explore the platform seemed overwhelming. Thankfully it doesn’t have to be.
In this simple, straightforward tutorial I’ll briefly guide you through dimensions and metrics- two fundamental, integral forms of data measurement that enable you to enhance your GA4 expertise.
What are dimensions?
Dimensions are the attributes or descriptions of data that are used to segment, organize and sort data. If you are looking at a GA4 report, these would be the rows that are represented in the chart. Dimensions are categorized into two groups: primary and secondary.
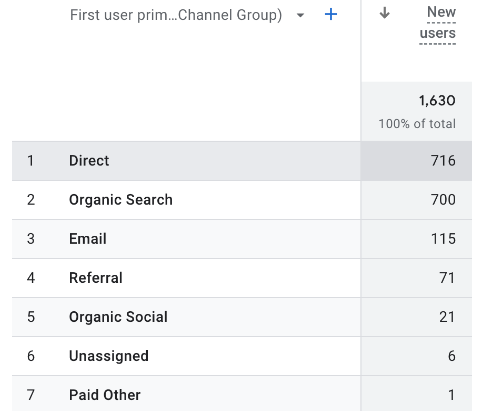
The primary dimension “First user primary channel group” listed below contains specific dimension values such as: Direct, Organic Search, Email, etc. In order to access secondary dimensions, click the “+” sign next to the primary dimension to open up a pop-up window with the options listed. By choosing a secondary dimension you can drill down your data into more specific results.
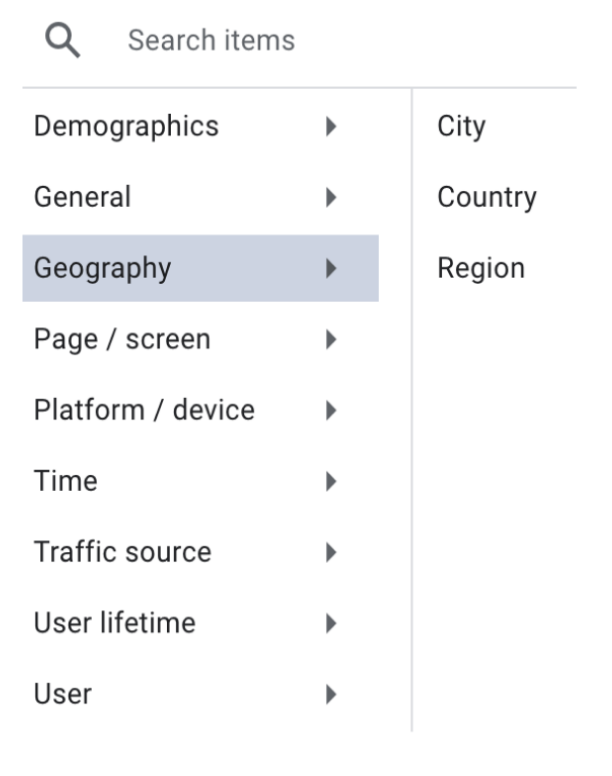
In this example below, if you select the Geography category and specifically select one of the three secondary dimension options, you can see how the user traffic acquisition compares for each city, country or region. Doing this helps to expand your realms of measurement and better understand where your traffic is coming from.
Here are a few significant dimensions to consider:
Source: shows where site traffic is coming from
Platform/Device: optimize user experience for different devices
Demographics: dimensions like Age and Gender provide greater insights into marketing efforts
Page/Screen: identifying the point where people entered website to determine which pages were successful in converting visitors
Event: provides detailed insights into specific user interactions, and helps to understand user preferences and behavior
What are metrics?
Metrics are quantitative data measurements that show how a website or digital product performs. They are typically presented through number values in columns in a Google Analytics report. Metrics answer the “how” questions of digital marketing, and can provide helpful insights that can lead to making informative marketing decisions.
In order to access more in depth information, click on the ‘Reports’ tab of the GA4 interface where you can see an overview of each life cycle: ‘Acquisition’, ‘Engagement’, ‘Monetization’ and ‘Retention’.
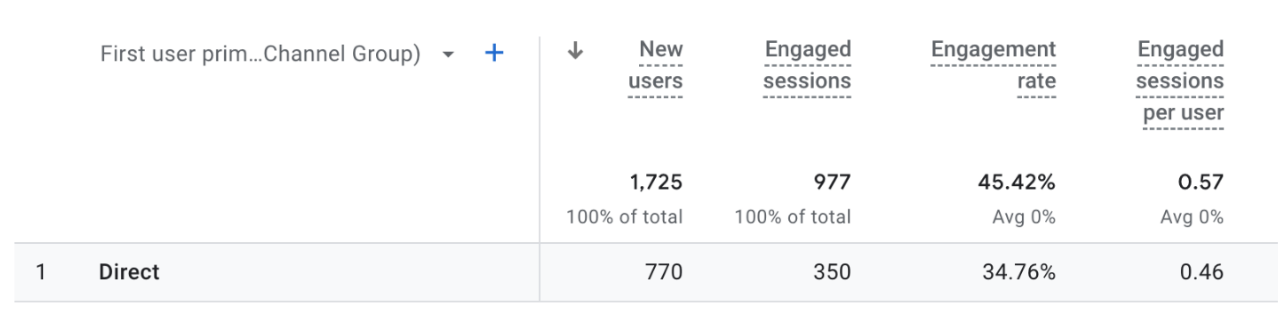

Here are a few significant metrics to consider:
Session: period of user’s interaction that can last up to 30 minutes of activity
Engaged Session: session that lasts 10 seconds or longer, one or more conversion events, or two or more page views
Bounce Rate: percentage of sessions where users didn’t have an “engaged session”
Engagement Rate: percentage of engaged sessions (calculation: engaged sessions/total sessions)
Why are metrics and dimensions important to a digital marketer?
Now that we have touched on these two key components of GA4, it’s time to apply what we’ve learned to the real business world and consider their importance.
Looking at dimensions, these attributes are useful and important in determining your website’s performance, the behavior of your audience and add depth to your data analysis.
For example, say you wanted to improve your blog content strategy and understand what your users’ interests are. By evaluating different aspects of user traffic through landing pages and exit pages, you can better comprehend what blogs your users are flocking to and their patterns of behavior.
With metrics, these numbers serve as indicators for the relative success of your marketing efforts.
To give an example of metrics in action, let’s consider the objective of tracking return on investment. If you want to see the financial results of your marketing campaigns, you can analyze certain metrics related to revenue and cost.
Conclusion
In summary, it’s evident that metrics and dimensions are vital to understand and grow your knowledge of how Google Analytics works. By utilizing qualitative data in dimensions effectively, you can gain a complete picture of what drives people to your site. Conversely, the ability to leverage quantitative data through the metrics listed above to your advantage can produce helpful insights to help grow your business or website.
I hope that this guide was helpful to you and gives you a better understanding of how metrics and dimensions function within Google Analytics!
